Navigating the world of credit cards can be complex, especially when understanding the various fees associated with them. From seemingly small annual fees to potentially hefty late payment fees and foreign transaction fees, these charges can significantly impact your credit score and overall financial health. This article will serve as your comprehensive guide to decoding these credit card fees, explaining what each one entails and providing actionable strategies to minimize or entirely avoid them.
Understanding credit card fees is crucial for responsible credit card management. Many cardholders are unaware of the various charges they might incur, leading to unexpected expenses and impacting their budget. We’ll delve into common credit card fees, including balance transfer fees, cash advance fees, and over-limit fees, offering clear explanations and practical tips on how to avoid them. By the end of this article, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to make informed decisions and choose a credit card that best suits your financial needs while minimizing unnecessary fees.
Annual Fees vs Transaction Fees
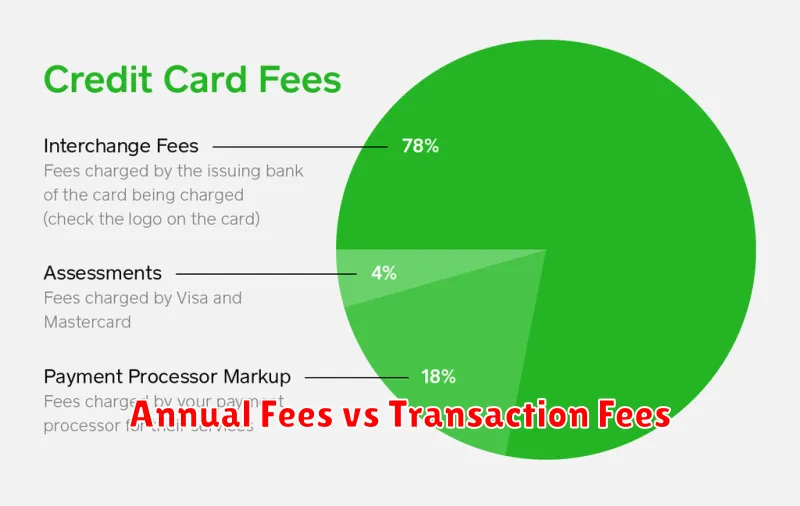
Understanding the difference between annual fees and transaction fees is crucial for choosing the right credit card. Annual fees are recurring charges levied by the card issuer each year for the privilege of holding the card. These fees can range from minimal to substantial, depending on the card’s features and benefits.
Transaction fees, on the other hand, are associated with specific card uses. These can include foreign transaction fees (charged for purchases made in foreign currencies), balance transfer fees (for moving debt from another card), and cash advance fees (for withdrawing cash from an ATM using your credit card). Unlike annual fees, transaction fees are only incurred when the specific transaction occurs.
Choosing between cards with annual fees and those without often involves weighing the benefits offered by the card against the cost of the annual fee. A card with a high annual fee may offer substantial rewards or perks that offset the cost, while a no-annual-fee card typically offers fewer benefits.
Carefully reviewing the fee schedule of any credit card before application is essential. Consider your spending habits and determine which type of fee structure aligns better with your financial goals. If you are a minimal spender, a no-annual-fee card is generally preferable. For frequent high-value purchases or those using specific card benefits, an annual fee card might prove more cost-effective in the long run.
Understanding Late Payment and Overlimit Charges
Late payment charges are fees incurred when you fail to make your minimum credit card payment by the due date. The amount of the fee varies by issuer, but it can significantly impact your credit score and overall cost of borrowing. Many issuers charge a flat fee, while others calculate a percentage of the missed payment.
Overlimit charges occur when your spending exceeds your credit limit. Credit card companies may assess a fee for exceeding the pre-approved spending limit, even if the overage is only by a small amount. These fees can add up quickly, especially with repeated occurrences. It’s crucial to track your spending diligently to avoid such charges.
To avoid these fees, it’s essential to pay your bills on time and monitor your spending closely to stay within your credit limit. Setting up automatic payments can help ensure on-time payments. Consider using budgeting tools or apps to track expenses and prevent overspending.
Foreign Transaction Fees Explained
Foreign transaction fees are charges levied by your credit card issuer when you make a purchase in a foreign currency. These fees typically range from 1% to 3% of the transaction amount.
The fee covers the cost of converting the foreign currency to your home currency. While the exact exchange rate used will vary, it’s often less favorable than what you might find through other means.
Avoiding these fees is possible. Some credit cards offer no foreign transaction fees. Look for this feature when choosing a card, or consider using a credit card specifically designed for international travel. Prepaid travel cards can also be a helpful alternative.
Understanding these fees is crucial for budgeting and managing your finances while traveling internationally. By researching your options and choosing wisely, you can significantly reduce or eliminate these often-overlooked costs.
Balance Transfer Fees and When to Use Them
A balance transfer allows you to move your existing credit card debt to a new card, often with a lower interest rate. However, most cards charge a balance transfer fee, typically a percentage of the amount transferred (e.g., 3-5%).
When to use a balance transfer: Consider a balance transfer if you can significantly reduce your interest rate and pay off the debt within the introductory 0% APR period. Carefully calculate the fee against the potential savings from lower interest; the savings should outweigh the fee to make it worthwhile. Be mindful of the balance transfer’s eligibility requirements and any associated penalties for failing to meet them.
When to avoid a balance transfer: Avoid balance transfers if the interest rate savings are minimal, the fee is high, or you don’t have a solid plan to repay the debt within the introductory period. The fees can quickly negate any benefit from a lower interest rate, potentially making the situation worse.
How to Avoid Unnecessary Fees
Understanding your credit card’s fee structure is crucial to avoiding unnecessary charges. Carefully review your cardholder agreement to identify potential fees, such as late payment fees, over-limit fees, and foreign transaction fees.
To avoid late payment fees, set up automatic payments or reminders to ensure timely payments. Staying within your credit limit prevents over-limit fees. Consider a credit card with no foreign transaction fees if you plan to use it internationally.
Be mindful of balance transfer fees if you’re transferring balances. Compare offers from different banks, factoring in any potential fees. Read the fine print regarding cash advance fees and interest rates, opting for regular purchases over cash advances whenever possible.
Regularly monitor your statements for any unauthorized transactions or unexpected fees. Contact your credit card company immediately if you identify any discrepancies or errors. Choosing a credit card with transparent and competitive fee structures can significantly minimize the risk of unforeseen charges.
Fee Waiver Tips and When to Call Your Issuer

Knowing when to contact your credit card issuer is crucial for successfully securing fee waivers. Proactive communication is key. Don’t wait until a fee appears on your statement; contact them before the fee is assessed, if possible.
Be polite and persistent. Clearly explain your situation, emphasizing any extenuating circumstances that justify a waiver. Highlight your positive credit history and long-standing relationship with the issuer (if applicable). Keep detailed records of all communication, including dates, times, and the representative’s name.
Consider calling when you face unforeseen circumstances such as job loss, medical emergencies, or natural disasters that significantly impact your ability to pay. These situations often increase the likelihood of a fee waiver. Also, be prepared to negotiate; sometimes a partial waiver is better than none.
If your initial request is denied, don’t give up. Politely reiterate your request, providing any additional supporting documentation you may have. If the issuer remains inflexible, consider escalating your complaint to a supervisor or exploring dispute resolution options through your card network (Visa, Mastercard, etc.).
Reading the Fine Print: Why Details Matter
Understanding credit card fees requires meticulous attention to detail. Ignoring the fine print can lead to unexpected charges and significant financial burdens. Credit card companies often bury crucial information within lengthy terms and conditions, making it easy to overlook important details regarding interest rates, annual fees, late payment penalties, and foreign transaction fees.
Carefully reviewing the terms and conditions before signing up for a credit card is paramount. Pay close attention to the definitions of key terms, the calculation methods for interest, and any conditions that might trigger additional charges. Understanding these details empowers you to make informed decisions and choose a card that aligns with your spending habits and financial goals.
Failing to read the fine print can result in significant financial losses over time. Even seemingly small fees can accumulate rapidly, especially if you carry a balance or make frequent transactions. By dedicating time to understanding the details, you can avoid unnecessary costs and maintain better control over your finances.